Catch up on Microservices March 2023. Register and get started on demand.
Microservices is an approach that builds a complex application from multiple small components. Learn about how it works, the pros and cons, and its benefits.
What Are Microservices?
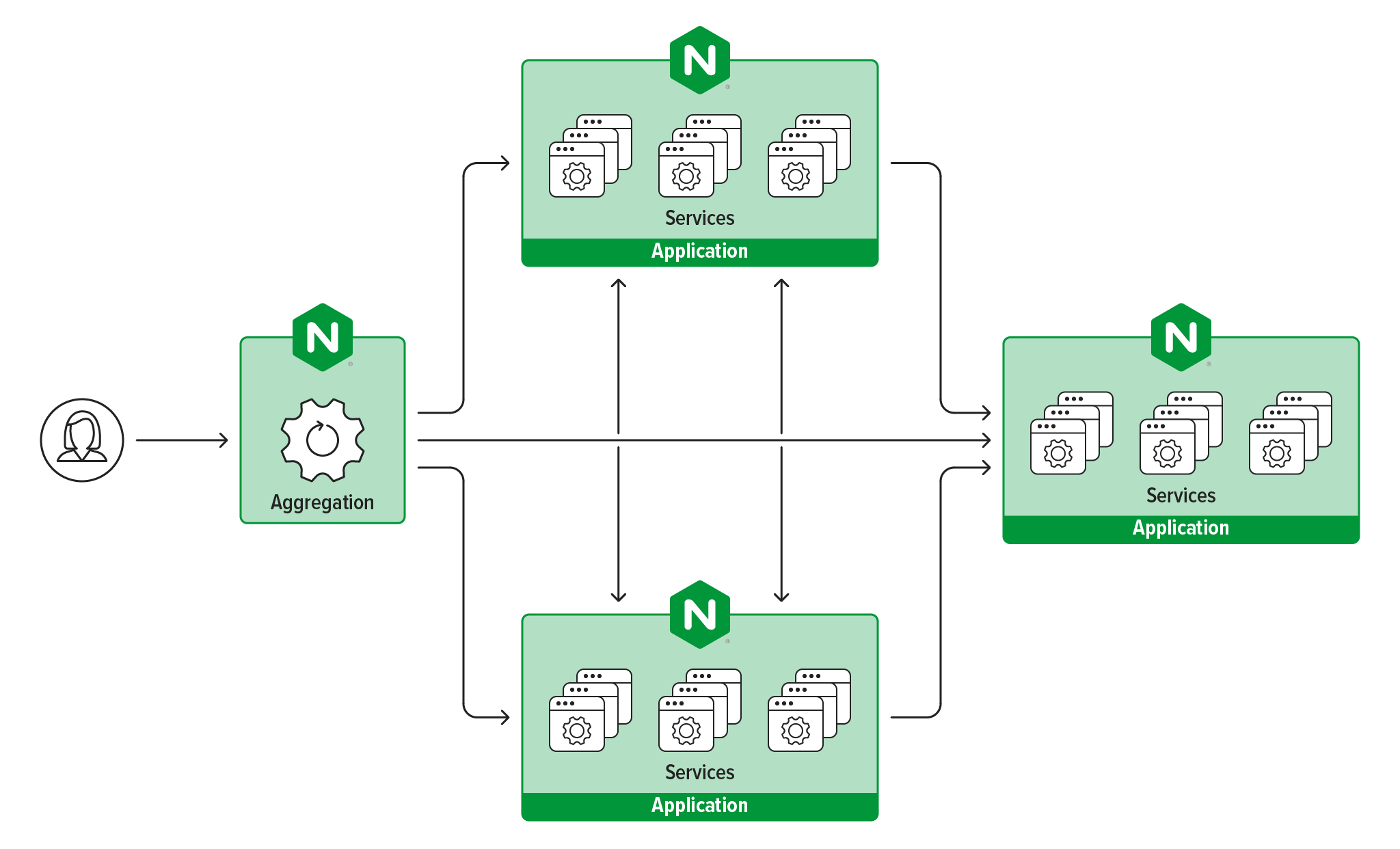
Microservices is an approach to software architecture that builds a large, complex application from multiple small components that each perform a single function, such as authentication, notification, or payment processing. Each microservice is a distinct unit within the software development project, with its own codebase, infrastructure, and database. The microservices work together, communicating through web APIs or messaging queues to respond to incoming events.
Videos on Microservices
Why Microservices Architecture?
In a traditional monolithic architecture, all of an application’s functionality is implemented in a single codebase. This has a few drawbacks:
- As the application becomes more complex, it becomes difficult for any one developer to understand the entire codebase. New developers face a steep learning curve during onboarding. One solution is to assign different functional modules to separate developers or teams. That makes it easier for developers to become experts about their own code, but harder to track the dependencies on other modules. This increases the chance that changes in one module break other modules.
- When you need to add or enhance functionality, you must compile and test the entire application to verify that the change doesn’t break compatibility between modules. Then you have to deploy the entire application as a single binary.
A microservices architecture instead divides application functionality among a set of independent microservices, making CI/CD much easier. Microservices are faster to develop and much easier to understand and maintain. Each service can be developed separately by a team that is focused just on that service. The team can choose the programming language, development platform, and database that best suits the microservice. Microservices are typically packaged as containers to further simplify deployment.
Microservices are loosely coupled, meaning they have no dependencies on the internals of other microservices. Instead they communicate with each other via API. As long as the API exposed by each microservice remains backward compatible, changes to one microservice don’t require updates to any others.
In short, developers who want to make changes in a microservice architecture can do so within an individual microservices container, whereas developers operating within a monolithic architecture face the time-consuming task of potentially having to rewrite their entire stack.
Who Is Using Microservices?
Technology teams that must quickly respond to changing business demands are turning more frequently to microservices architectures. Developers are primarily leading this charge, thanks in large part to more organizations handing them the permissions necessary to choose application and delivery tools. According to a 2020 survey of NGINX users, more than half of respondents are using microservices in some or all of their apps. And in 2022, more NGINX users who worked for companies that were transitioning away from monolith systems reported an adoption of microservices thanks in part to the scalability that container orchestration allows.
Microservices 101: Pros and Cons
Microservices can save you time, money, and resources by transforming your old monolithic applications into a more flexible, secure, and efficient architecture. The following is a summary of strengths and vulnerabilities, which can affect application performance and design.
- Developers have the freedom to independently develop and deploy services, resulting in faster decision making.
- Due to the small size and autonomy of microservices, a microservices based approach results in shorter development cycles, as different teams can be implementing different services simultaneously. Dependency between teams is usually reduced or even eliminated.
- Microservices can easily be deployed on containers, resulting in less overhead and improved portability across different environments.
- Developers can embrace modern DevOps practices such as automated CI/CD pipelines, because microservices integrate easily with CI/CD tools.
- It’s easy to scale apps, “right‑sizing” them to the level of demand, as each service is usually elastic.
- Microservices are easier to build, test, and maintain.
- Services are organized around business capabilities.
- Developers can adopt the technology most suited for a specific service.
- Fault isolation is easier – If one microservice fails, others continue to function.
- A microservices architecture involves added complexity, as developers have to mitigate fault tolerance, reduce network latency, deal with varying programming languages, and load balance across multiple services.
- Troubleshooting microservices can be cumbersome and complicated, because of their distributed nature.
- Increasing the number of microservices in an application increases the effort required for effective integration and management.
- Dealing with multiple databases can be painful.
Is an API a Microservice?
In short, no. APIs alone are not microservices. However, they are increasingly being integrated into microservices architectures as the mechanism for communication within the application. A microservice’s functionality is exposed as a set of API endpoints and other microservices invoke that functionality by making an API call against the appropriate endpoint.
Why Use Containers to Run Microservices?
Containerized platforms allow developers to isolate, scale and deploy microservices in the most efficient, infrastructure-agnostic way and with minimal disruption to users. Consider a scenario where a single cluster of load balancing and traffic routing servers is deployed in front of your applications. With a static public IP address published in DNS, clients can address their requests to this stable entry point and it is forwarded to the appropriate container. If you add or remove those containers, you only need to update the internal address to direct those requests to the new IP address. You can also publish them internally through DNS.
Microservices Examples
Microservices Accelerate Seamless Security Transition in Highly Regulated Industry
A multinational corporation in a heavily regulated industry must upgrade its systems on a prescribed schedule to remain compliant with evolving standards and best practices. This company’s portfolio of applications handles millions of transactions every day through its systems. For years, the company remained compliant with industry requirements even during open source upgrades and integration of a third-party security plug-in. However, during a recent upgrade, the company experienced problems due to a mutex issue with the plug-in. The company was already researching moving away from a data center to the AWS public cloud, and the security plug-in issue prompted them to move to a microservices architecture. This solution was cheaper and enabled the company to be both compliant and secure right away.
Read about the journey to microservices in this customer success story.
Blog
- Introduction to Microservices (7-part series)
- Refactoring a Monolith into Microservices
- Reduce Complexity with Production-Grade Kubernetes (10-part series)
eBooks and Reports
- Microservices Up and Running
- Get Me to the Cluster
- Managing Kubernetes Traffic with F5 NGINX: A Practical Guide
- A Stress-Free Roadmap to Application Modernization
Success Stories and Use Cases
- Tipico Relies on NGINX Plus to Transition to Microservices and Deliver Reliable Performance in the Cloud
- Sistic Lowers Costs by 80% and Accelerates Go-to-Market Speed with NGINX Plus
- Team Fresh Optimizes Microservices and Cloud Environments with F5 NGINX Plus
- Canal+ Upgrades from NGINX Open Source to NGINX Plus to Support Its Move to Microservices
- EPAM Uses NGINX Plus to Build Windows Containers Five Years Before the Rest of the World
